
The research group lead by Prof. SHEN Xu in Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, CAS has been studying the molecular mechanisms of anti-diabetic compounds based on the structural and cellular levels. Their latest finding on the discovery of a natural product as retinoic X receptor antagonist has been published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21084305).
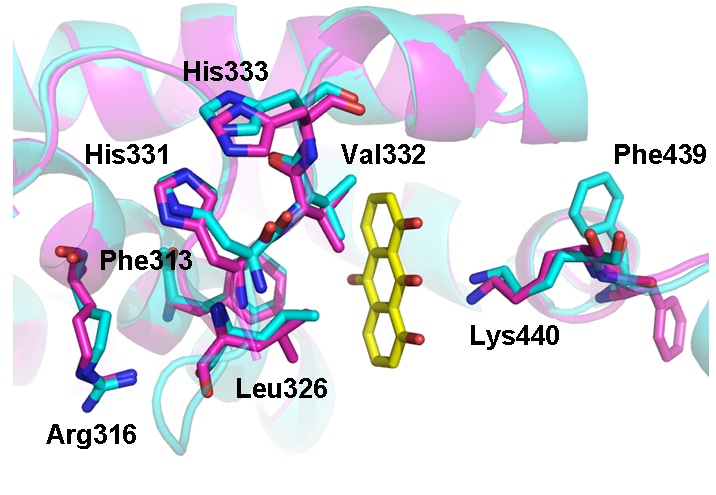
Retinoic X receptor (RXR) is a promising target for drug discovery against cancer and metabolic syndromes. A specific RXR antagonist danthron was screened from the traditional Chinese medicine rhubarb. Danthron could represse all the tested RXR-involved response elements transcription, including RXRE, PPRE, FXRE and LXRE. The determined crystal structure of danthron-bound RXR-LBD suggested a new mechanism for danthron antagonism to tetrameric RXR. These findings were expected to supply new insights into the structural basis of RXRa antagonist for its further potential therapeutic application. The ability to improve insulin sensitivity in vivo has made danthron a promising lead compound for the development of anti-diabetic drugs and supplied useful information for understanding the pharmacological mechanisms of rhubarb.
This work was supported by the State Key Program of Basic Research of China (grants 2010CB912501, 2007CB914304, 2009CB918502), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grants 30925040, 30890044, 10979072), Key New Drug Creation and Manufacturing Program (2009ZX09301-001), Science foundation of Shanghai (08431902900), E-Institutes of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (E09013) and Foundation of Chinese Academy of Sciences (grants KSCX2-YW-R-168, SCX1-YW-02-2).

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

